DSB-R100
Frequently Asked
Questions (FAQ)
- What is the
DSB-R100?
- What's the
difference between MP3 and Wave format?
- How do I
record and play back my music?
- How do I
record a Wave file?
- How do I
convert the recorded wave files to MP3 audio format?
- Does FM
recording and MP3 conversion process occur at the same time?
- If not, what
format the does the resultant FM recording take?
- What's the
MP3 conversion bitrate of the unit?
- Why won't my
DSB-R100 USB Radio work?
- Windows 98
SE
- Windows
2000
1. What is the DSB-R100?(Back to
top)
The DSB-R100 is a USB PC Radio that has the following features:
- True Plug and Play installation featuring a USB connection
- Full FM Radio reception (no AM)
- Compliant with USB Specification 1.1
- Dipole FM Antenna
- Recording software included in the box
- MP3 Conversion Software included in the box
The DSB-R100 is compatible with Windows 98 and Windows 2000, making
it possible for you to listen to your favorite radio station, record
songs to your hard drive and play them back at will while simultaneously
working on your computer. Just install the software and plug the
DSB-R100 into a USB port on your computer. The DSB-R100 is a receiver,
it uses your computer's sound system to play the music.
The DSB-R100 includes software MP3 Compressor which enables you to
record your favorite programs or music in the MP3 format for playback
whenever you want. State of the art radio technology with leading edge
custom channel presets and digital sound brings a new level of FM
broadcasts directly to your computer.
Displayed in a sleek case, the DSB-R100 has a flexible and detachable
antenna. The D-Link DSB-R100 takes very little desk space and is easily
transported. It draws its power from your computer's USB port, so its
compatible with your laptop too.
_______________________________
2. What's the difference between MP3 and Wave
format?(Back to
top)
MP3 and Wave are both formats for recording CD quality audio files.
MP3 is a newer format than Wave that enables you to create much smaller
files while still retaining CD quality sound.
MP3 compresses audio files, which tend to be very large, into smaller
files while still retaining CD quality sound. A minute of music encoded
in MP3 requires roughly one tenth the space that older formats like Wave
need. A wave file that would take hours to download because of its size
can be converted to MP3. The MP3 file would be much smaller and
therefore could be transferred in a fraction of the time.
Wave is an older file format. It does not have the compression
capability of MP3 and therefore is less desirable, especially in cases
where file size needs to be kept small.
_______________________________
3. How do I record and play back my music?(Back to
top)
The music must first be recorded in Wave format and then converted to
MP3. This method has several benefits:
- MP3 files can be as small as 1/12 the size of the original Wave
file due to its high compression ratio.
- MP3 files have CD quality sound without degradation.
- MP3 is the standard audio file format for the Internet
Before recording a Wave file, make sure the correct format of the
file is specified. Wave format refers to the sound channel, Sampling
Rate and Size of the file.
To specify the wave format:
- Select Record Setting in the Options menu and
Choose Wave Format dialog box appears.
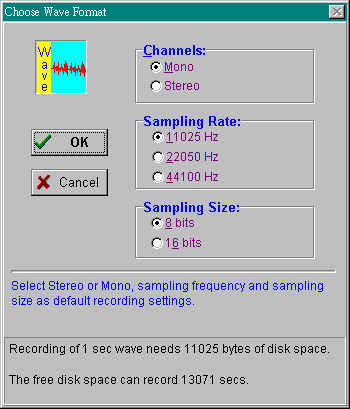
- Select the format for the wave file.
Select Mono for one sound channel and Stereo for two sound
channels.
Select 11025Hz for voice, 22050Hz for cassette and 44100Hz for CD
quality recording.
Select 8 bits for cassette and 16 bits for CD sound quality.
- Choose OK.
There is a trade-off between the quality of a wave file and the
amount of storage space required for the file. A wave file with better
sound quality requires a larger storage space because of its high
sampling rate. The message in the dialog box will inform you how much
free disk space is available for recording.
_______________________________
4. How do I record a Wave file?(Back to
top)
To record a wave file:
Click Record button. The animated tape recorder will revolve
the length and current location of recorded file will be displayed.
_______________________________
5. How do I convert the recorded wave files to MP3
audio format?(Back to
top)
To convert a Wave file to an MP3 file, you need to install the MP3
Compression software on the CD ROM included with your DSB-R100 or download
and install Real Player or other applications that support MP3.
Wave files can be converted to MP3 files quickly and easily. In order
to play the wave file you will need to download and install Real Playerİ
or other applications that support MP3. You can download the application
at http://www.real.com/
and http://www.winamp.com/.
To convert a wave file to an MP3 file:
- Go to WaveFile and select Wave to MP3 utility.
- The Enhanced MP3 functions panel appears.
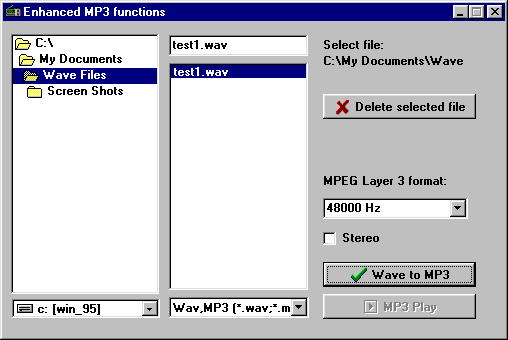
- Browse to the directory the wave file is in and select it the on
panel to the right.
- MPEG Layer 3 format
gives you several ranges to choose from.
Click on the down arrow and choose the sampling rate. 48000 Hz gives the
best sound but uses the most memory.
- Click on the Wave to MP3 button to convert the file to
MP3.
- Check the box marked Stereo for stereo sound.
- The MP3 Compressor panel gives you a status report on the file
conversion.
- Click Pause to stop the conversion.
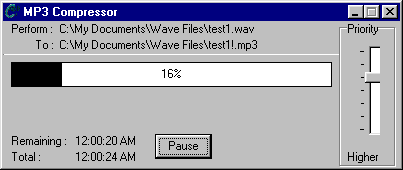
- Play the file using Real Player or another application that supports
MP3.
_______________________________
6. Does FM recording and MP3 conversion process
occur at the same time?(Back to
top)
No. It does not. The music must first be recorded in wave format. An
encoder is then used to convert wave files into MP3.
_______________________________
7. If not, what format the does the resultant FM
recording take?(Back to
top)
The FM recording is in the .wav format.
_______________________________
8. What's the MP3 conversion bitrate of the
unit?(Back to
top)
Using the included MP3 Compressor, the conversion bitrate from .wav
file is 128 kb/s. The user can define various sampling rates. However,
there are tradeoffs. 48000 Hz yields the best sound quality but uses the
most memory.
Bitrate is defined as the average number of bits that one second of
audio data consumes.
_______________________________
Next
Page |